In an article published in the journal Nature, researchers discussed the European project SIGNIFICANCE, which fought against the illegal trafficking of cultural heritage (CH) goods using an artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL) platform.
 Study: AI Fights Illegal Cultural Goods Trafficking. Image Credit: Michal Ninger/Shutterstock
Study: AI Fights Illegal Cultural Goods Trafficking. Image Credit: Michal Ninger/Shutterstock
This platform helped authorities identify, track, and block illegal online activities, enhancing law enforcement capabilities. It also provided contextual information about artifacts and utilized the HPC CyClone infrastructure for efficient computational tasks. Preliminary results showed a 10-15% increase in identifying illegal artifacts.
Background
Illegal trafficking of cultural goods remains a global challenge despite robust legislative frameworks like the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) 1970 and International Institute for the Unification of Private Law (UNIDROIT) 1995 conventions. Social media and e-commerce platforms have exacerbated this issue, making it difficult for law enforcement agencies to monitor and prevent illegal activities. Previous research has employed machine learning and image classification techniques to address these challenges, but gaps remain in the real-time detection and prevention of illicit trade, particularly across various online platforms.
The European project SIGNIFICANCE aimed to fill these gaps by utilizing AI and DL to develop a user-friendly platform that enabled authorities to identify, track, and block illegal activities online. The platform incorporated an ontology-based approach to provide comprehensive information about the cultural significance, provenance, and legal status of artifacts. By scraping data from the web, social media, and the dark web, SIGNIFICANCE enhanced the identification and prosecution of criminal networks, increasing the identified quantity of illegal artifacts by 10-15% annually.
Methodology and Implementation
The SIGNIFICANCE project employed a comprehensive methodology to combat the illicit trafficking of CH goods using advanced AI and DL techniques. The project involved several key steps.
- Data extraction and storage: Custom web crawlers scraped data from various online sources, including selling portals (Catawiki, and eBay), social media (Instagram and Facebook), and the dark web. Extracted data included images, descriptions, seller profiles, and transaction details, which were stored in a MongoDB database.
- CH database and data annotation: The collected data formed a dataset tailored for detecting illegal traffic. An ontology-based approach was used for data annotation, enhancing classification accuracy by incorporating domain-specific knowledge and relationships between artifact attributes.
- AI module: A convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture was employed for image classification. Artifacts were represented by multiple images and associated metadata. The classification approach included two stages, classifying the artwork among defined classes (coins, frescoes, icons, manuscripts, others) and then extracting specific features (location, period) based on the classification. The VGG16 neural network was used due to its proven reliability in classification tasks.
- SIGNIFICANCE platform: A user-friendly visualization platform allowed authorities to interact with and analyze results from the detection and prevention framework. The platform supported informed decision-making and targeted actions against illegal traffickers. It incorporated the CyClone HPC Infrastructure for computationally intensive tasks, optimizing computing time, resources, and cost-efficiency.
Results and Discussions
The implementation and evaluation of the SIGNIFICANCE Framework demonstrated its effectiveness in detecting and preventing the illegal movement of CH goods. The framework leveraged comprehensive data analysis, DL, ontology-based classification, and real-time monitoring through a tailored platform.
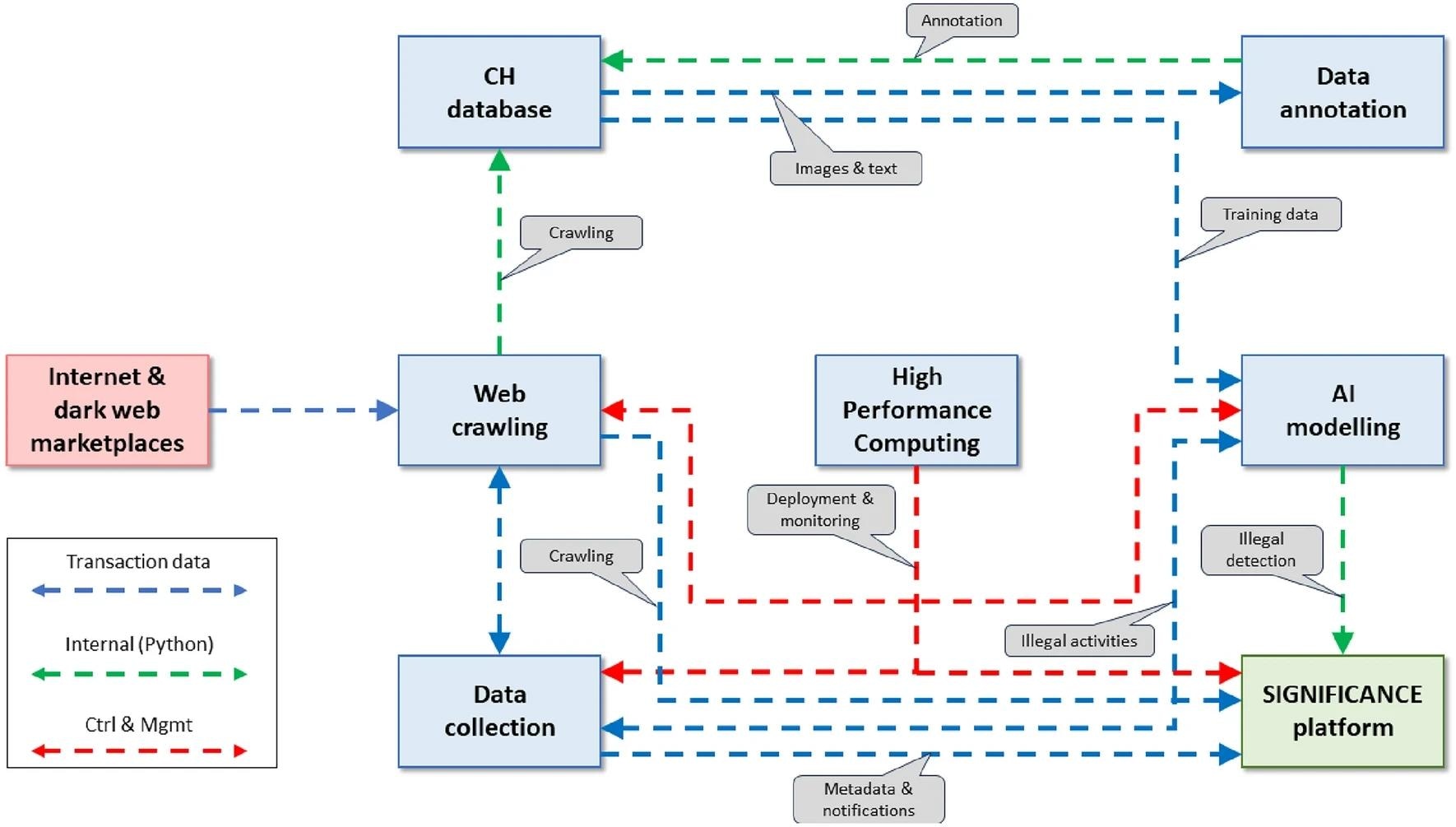 SIGNIFICANCE architecture detailing the interfaces between the different components as well as the data exchanged and functions between them. Image Credit: www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-65885-6
SIGNIFICANCE architecture detailing the interfaces between the different components as well as the data exchanged and functions between them. Image Credit: www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-65885-6
The AI module, employing a VGG16 neural network, was evaluated on classification accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. The dataset, split 80-20% for training and testing, showed promising results in classifying artifacts and their features despite limited samples. Notably, the system achieved significant performance in the initial classification phase and subsequent feature classification.
The SIGNIFICANCE platform provided interactive visualizations and dashboards, enabling users to explore data, detect unauthorized sales, and monitor illegal transfers of CH artifacts. The platform's user interface facilitated searches by keywords or AI-processed labels, enhancing the efficiency of identifying suspicious activities. The real-time monitoring capability proved effective in reporting cases and taking timely preventive actions.
Limitations included the current inability to automatically classify objects as legal or illegal. This required the synthesis of rules or the creation of annotated datasets, demanding expert validation from archaeologists, art historians, and cultural heritage specialists. The developed platform, however, aided experts in filtering and assessing objects, advancing toward the goal of early and automatic identification of illegal trade. The system’s scalability and integration with expert knowledge held promise for future improvements in combating illegal CH trade.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the researchers presented the results and findings of their research on detecting and preventing the illegal movement of CH goods through the SIGNIFICANCE Framework. Their approach, integrating DL, ontology-based classification, and real-time monitoring, proved effective in identifying illegal activities.
The visualization platform enhanced understanding and decision-making for law enforcement. Future work will focus on optimizing the DL model, expanding data sources, and ensuring ethical practices. Collaborations and a dynamic monitoring framework will further advance the field, creating robust solutions for safeguarding cultural heritage.
Journal reference:
- Malinverni, E. S., Abate, D., Agapiou, A., Stefano, F. D., Felicetti, A., Paolanti, M., Pierdicca, R., & Zingaretti, P. (2024). SIGNIFICANCE deep learning based platform to fight illicit trafficking of Cultural Heritage goods. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 15081. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65885-6, www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-65885-6