By merging AI-powered analytics with biochar engineering, scientists are fast-tracking eco-friendly solutions to lock away carbon, clean water, and build a sustainable future.

Research: Machine learning-enabled optimization of biochar resource utilization and carbon mitigation pathways: mechanisms and challenges. Image Credit: Rene Notenbomer / Shutterstock
Biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from organic waste, is gaining attention for its ability to enhance soil quality, purify water, and sequester carbon. A new review in Biochar X highlights how machine learning (ML) is reshaping biochar research, making it faster, smarter, and more effective in tackling climate change.
How Machine Learning Enhances Biochar Research
By analyzing large datasets, ML models such as random forests and deep neural networks can predict biochar yield, surface area, and pollutant removal efficiency with over 90% accuracy. This reduces costly trial-and-error experiments, allowing scientists to design biochars with tailored properties for environmental applications.
"Biochar has enormous potential as both a waste-to-resource pathway and a climate solution," said corresponding author Tao Zhang of China Agricultural University. "Machine learning gives us powerful tools to accelerate its development and maximize its environmental benefits."
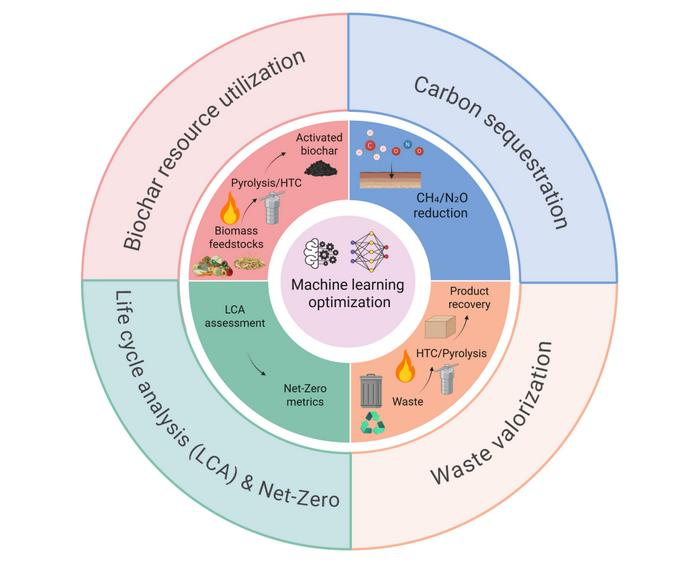
Machine learning-enabled optimization of biochar resource utilization and carbon mitigation pathways: mechanisms and challenges. Image Credit: Yusong Jiang, Shiyu Xie, Salah F. Abou-Elwafa, Santanu Mukherjee, Rupesh Kumar Singh, Huu-Tuan Tran, Jianshuo Shi, Henrique Trindade, Tao Zhang & Qing Chen
Environmental Benefits
The review finds that biochar use can cut greenhouse gas emissions by 20%–70% and sequester up to 90% of carbon, depending on production conditions.
Beyond climate mitigation, engineered biochars are being applied to:
- Clean polluted water
- Remove heavy metals and organic contaminants
- Capture microplastics
- Strengthen construction and energy storage materials
Challenges and Future Directions
The authors note that challenges remain, including the need for better data sharing, standardized reporting, and closer collaboration between environmental scientists and AI experts. Emerging techniques, such as deep learning, self-supervised learning, and life cycle assessment, are expected to enhance further the role of biochar in achieving global carbon neutrality and supporting a circular economy.
"This integration of machine learning and biochar is a clear example of how digital technologies can drive green innovation," Zhang said.
Source:
Journal reference: